

The plexus then provides an anastomosing network of capillary sinusoids that constitute the cortex’s vascular system. The short cortical arteries form the subcapsular plexus branches. Left suprarenal vein which drains into the left renal or inferior phrenic vein. Right suprarenal vein which drains directly into the inferior vena cava On the contrary, each gland is drained by a single vein, namely Inferior suprarenal artery - a branch of the renal artery Middle suprarenal artery - a direct branch of the abdominal aorta Superior suprarenal artery - a branch of the inferior phrenic artery
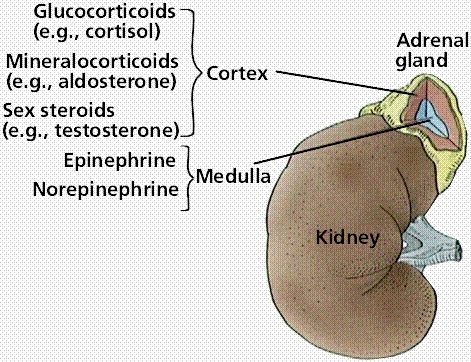
This could only be achieved due to several arterial branches entering the gland, which are derived from three major branches ( Figure 1) : The blood supply rate per gram of tissue for the adrenal gland is one of the highest. Arterial supply, venous & lymphatic drainage Gross appearance and microscopic architectureĪrterial supply, Venous & Lymphatic drainageĤ. In this chapter, the adrenals are discussed under the following headings: These two parts share the similarity in their location, apart from which they differ in their ontogeny, phylogeny, architecture, and function. Īdrenal glands have two major parts: the cortex and the medulla. In gross appearance, these are yellowish. These are endocrine glands, therefore, receive profuse blood supply via multiple arteries. The paired structure was termed “suprarenal”, another Latin word where “ supra” means “above”, by Jean Riolan the Younger in 1629.


Adrenal is a Latin word where “ ad” means “near”, and “ ren” means “kidney”. The adrenal glands were initially described in detail by Italian anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi in 1563–1564. These tissue masses are referred to as adrenal glands. The kidneys’ fibrous capsule (renal fascia) wraps a wedged glandular and neuroendocrine tissue to its upper pole.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
